Imagine waking up one day to know that your heart—the very engine of your body—is malfunctioning. Didn’t mean to scare you but the facts are sobering: heart disease is now the biggest cause of death worldwide, killing approximately 18 million people every year. In India, the burden is considerably greater, with heart disease accounting for more than one-quarter of all deaths. It’s a silent epidemic, fuelled by our fast-paced, stressful lives, and exacerbated by increased rates of diabetes, hypertension, and poor diets.
For many years, treating a blocked heart required invasive treatments such as bypass surgery or angioplasty. But what if there was a way to improve your heart health without undergoing surgery? A non-invasive heart treatment that does not require you to confront the intimidating hazards of surgery while promising to improve blood flow and maybe eliminate those deadly blockages. It seems almost too good to be true, doesn’t it? But the science behind EECP is both fascinating and encouraging. In this post, we’ll look at how EECP works and how it could be a game changer for people with heart disease.
Before we get into how EECP treatment works, it’s important to understand what heart blockages are. Coronary arteries provide blood to the heart muscle, and when these arteries are blocked, the accumulation of plaque (a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other chemicals) restricts the flow of blood to the heart. This disorder, known as coronary artery disease (CAD), can cause angina (chest pain), shortness of breath, and even heart attacks.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the EECP Treatment?
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) is a non-invasive treatment that increases blood flow to the heart. It is frequently indicated for patients with angina who are not candidates for invasive procedures such as bypass surgery or angioplasty. EECP works by increasing the delivery of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, which can help alleviate or eliminate heart disease symptoms.
How Does EECP Treatment Transform Heart Health?
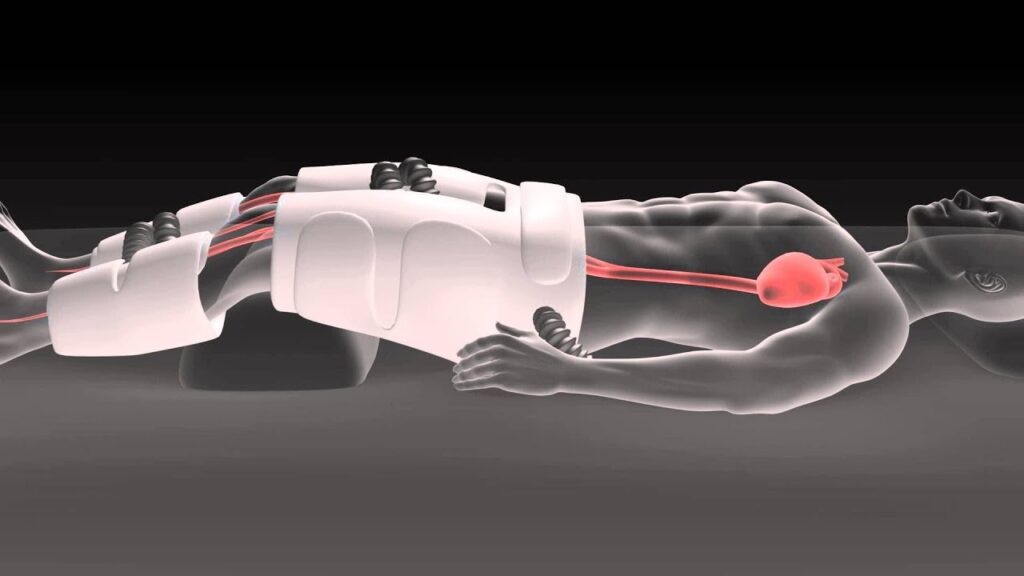
EECP treatment consists of a series of sessions in which the patient lies on cuffs wrapped around their legs and lower body when they are placed on a treatment table. These cuffs, like blood pressure cuffs, are attached to a machine that inflates and deflates them in response to the patient’s heartbeat. The inflation of the cuffs during the heart’s resting phase (diastole) forces blood back into the heart, improving blood flow to the coronary arteries. During the heart’s active phase (systole), the cuffs rapidly deflate, lowering the workload on the heart.
- EECP aims to enhance blood flow to the heart muscle. The treatment improves venous return, or the amount of blood returning to the heart, by inflating the cuffs in time with the heart’s beat. This enhances the blood flow. It can help open up existing collateral vessels (small blood channels) and promote the formation of new ones, thereby bypassing clogged arteries.
- Reduced Workload on the Heart: By deflating the cuffs during systole, EECP lowers the resistance that the heart confronts when pumping blood. This decrease in effort can assist lower the heart’s oxygen demand, which is especially advantageous for people with angina.
- Collateral Circulation Promotion: EECP has the potential to stimulate the creation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. These new veins can form natural bypasses around blocked arteries, increasing total blood flow and lowering heart disease symptoms.
- Improvement in Endothelial Function: EECP has also been proven to improve endothelial function, which is the inner lining of blood vessels. Healthy endothelial function is critical for controlling blood pressure and preventing blood clots, both of which are essential for heart health.
EECP vs Traditional Treatments
While bypass surgery and angioplasty have long been recognised as effective therapies for heart blockages, they carry major risks and require prolonged recovery times. Bypass surgery, in particular, requires open-heart surgery, which can be scary for many people. The surgery demands making a large incision in the chest to access the heart, which not only increases the danger of infection but also needs a lengthy healing period, frequently several weeks or even months. According to some research, the mortality rate for coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) is 1-3%, depending on the patient’s overall condition and the procedure’s complexity. Complications such as stroke, heart attack, and infections may also develop during or after surgery.
Angioplasty, while less intrusive, still requires threading a catheter through the arteries to the point of blockage. This treatment, while less daunting than open-heart surgery, is not without hazards. Patients who undergo angioplasty may encounter problems including as haemorrhage, blood vessel damage, and, in certain situations, the necessity for emergency bypass surgery if the artery is significantly damaged during the treatment. Furthermore, there is a danger of restenosis, which occurs when the artery narrows again after the treatment and requires another intervention.
In contrast, Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) provides a completely non-invasive alternative. There is no need for surgery, no anaesthesia, and most importantly, no significant recovery period. The technique entails the patient laying on a bed with cuffs wrapped around the legs and buttocks that inflate and deflate in time with the heartbeat. This action helps to increase blood flow to the heart, lowering its workload and encouraging the formation of new blood vessels, known as collateral circulation, around the blocked arteries.
One of the most important benefits of EECP is its safety profile. Unlike bypass surgery or angioplasty, EECP carries no significant hazards. There is no incision, no chance of infection, and no risks associated with surgical procedures. The treatment is often delivered in a series of outpatient appointments, allowing patients to return to normal activities practically immediately. This simplicity makes EECP a viable choice for people with hectic schedules or who cannot afford extended hospital stays.
Who Can Benefit From the EECP?
EECP is especially advantageous to those who:
- Have Chronic Angina: Many individuals who have not reacted well to medication find relief with EECP. The medication can greatly lower the number and severity of angina events.
- Are Not Candidates for Surgery: For patients who are unable to undergo bypass surgery or angioplasty due to other medical issues, EECP provides an option.
- Patients who have undergone bypass surgery or angioplasty but are still experiencing symptoms may benefit from EECP.
- Seek a Non-Invasive Alternative: For people who want to avoid surgery and its hazards, EECP is a safe and effective option.
The Benefits of EECP Treatment
- Non-invasive and painless, requiring no surgery or needles.
- Many patients report a considerable improvement in their quality of life following EECP. Angina symptoms are lessened, energy levels rise, and patients frequently discover that formerly difficult physical activities are now possible.
- No Recovery Time: Unlike surgical treatments, EECP has no recovery period. Patients can continue their regular activities immediately following each session.
- Long-Term Benefits: Studies have shown that the benefits of EECP can remain for several years following treatment, making it a viable alternative for controlling cardiac disease.
- Reduced risk of complications: Although non-invasive, the risk of problems is substantially lower than with surgical treatments. There is no risk of infection, haemorrhage, or anaesthesia-related complications.
EECP Treatment Process
The average EECP treatment program consists of 35-40 one-hour sessions spaced across seven weeks. However, the number of sessions required may differ based on the patient’s condition and reaction to treatment. Patients are continuously watched during each session, and treatment is changed as needed to provide the best possible results.
Conclusion
EECP is a novel, non-invasive treatment that provides significant benefits to individuals with heart blockages. EECP can effectively treat heart disease symptoms and enhance overall quality of life by increasing blood flow to the heart, stimulating collateral circulation, and reducing the heart’s strain. As more patients seek alternatives to typical surgical treatments, EECP is emerging as a promising treatment option with long-term benefits. If you or a loved one suffers from cardiac disease, it may be worth considering EECP treatment in Delhi/NCR as part of your treatment plan. Consult your healthcare physician to find the best approach for your specific needs.
References: